BAIN MUSC 726T
Tuning Theory
Mathematical Definitions
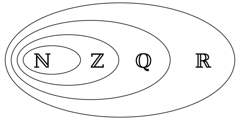 Number
Sets
Number
Sets
- Natural numbers (
 )
{WP}
)
{WP}
- Integers (
 ) {WP}
) {WP}
- Rational numbers (
 ) {WP}
) {WP}
- Real numbers (
 ) {WP}
) {WP}
- Prime numbers {WP; MW;
OEIS}
Arithmetic
- Arithmetic {MW; WP}
- Operations
- Addition (+)
{MW;
WP}
- Subtraction (-)
{MW;
WP}
- Multiplication (x,
or *) {MW;
WP},
see also dot
operator
- Division (÷,
or /) {MW; WP}
- Exponentiation (see
below)
- Order of Operations: PEMDAS
{WP}
Number Theory
- Prime numbers, the "atoms" of arithmetic {WP; OEIS}
2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31,
37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71, 73, 79, 83, 89, 97, ...
- Sieve of Eratosthenes {WP}
- Fundamental theorem of arithmetic {WP;
MW}
- Factorization {WP; MW}
Number Sequences
- Natural numbers, or positive integers: an arithmetic
progression with a common difference of 1 {WP; OEIS}
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, ...
- Powers of 2: a geometric
progression with a common multiple of 2 {WP; OEIS}
1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, ...
- Harmonic sequence: a harmonic
progression with a(n) = 1/n {WP;
MW}
1, 1/2, 1/3, 1/4, 1/5, ...
- Square numbers {WP; MW;
OEIS}
0, 1, 2, 4, 9, 16, 25, ...
- Triangular numbers {WP;
MW;
OEIS}
0, 1, 3, 6, 10, 15, 21, ...
- Fibonacci numbers {WP;
MW;
OEIS}
0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, ...
Sloane, The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer
Sequences {OEIS} (Sloane 1964)
Fractions {Calculator: Wolfram
Alpha}
- Fraction, represents a part of a single whole {WP; MW}
a/b
- Denominator (b)
- Quotient (q = a/b)
{WP}
- Ratio, compares the size of two or more quantities {WP; MW}
a:b, a:b:c, etc.
- Reciprocal, The reciprocal of x is 1/x {WP;
MW}
e.g., the reciprocal of 2 is 1/2
- Superparticular ratio, (n+1)/n, where n is a
positive integer {WP}
e.g., 2/1, 3/2, 4/3, 5/4, 6/5,
7/6, 8/7, 9/8, 10/9, etc.
- Reduced fraction, a fraction's simplest form {WP}
e.g., 4/2 = 2/1; 6/4 = 3/2, 12/6 =
2/1, 80/64 = 5/4, etc.
- Ratio under octave reduction {XW}
e.g., 3/1 = 3/2, 4/1 = 2/1, 5/1 =
5/4, 6/1 = 6/4 = 3/2, 7/1 = 7/4, etc.
- Multiplying a fraction by another fraction {WP}
e.g., 3/2 ×
4/3 = 2/1; 9/8 ×
9/8 = 81/64; 9/8 × 5/4 = 45/32, etc.
- Dividing a fraction by another fraction {WP}
e.g., 2/1 ÷ 4/3 = 2/1 ×
3/4 = 6/4 = 3/2
- Decimal expansion {MW}
- 3/2
= 1.5
- 5/4
= 1.25
- 9/8
= 1.125
- 81/64 =
1.265625
- Rounding {WP;
MW}
- 4/3 ≈
1.3 (rounded to one decimal place)
- 5/3 ≈
1.67 (rounded to two decimal places)
- 10/9 ≈ 1.111 (rounded
to three decimal places)
- Approximation {WP; MW}
- Significant digits {WP}
- Rounding errors {WP}
- Multiple {WP}
e.g., 6 is a multiple of 2, because 2 x 3 = 6
- Factor, or divisor {WP}
e.g., 2 is a factor of 6, because 2 x 3 =
6
- Least common multiple (LCM) {WP;
Calculator: Wolfram
Alpha}
e.g.,
LCM (4, 6) = 12; LCM (3, 5) = 15; LCM (4, 5, 6) = 60, etc.
- Lowest common denominator (LCD) {WP;
Calculator: Calculator
Soup}
e.g., LCD (1/2, 2/3) = 6; LCD
(5/12, 11/18) = 36; LCD (1/2, 1/3, 1/4) = 12; etc.
Exponentiation
- Exponentiation (^) {WP}
e.g., 2^3 = 2 × 2 × 2 = 8;
e.g., 12-tet:
2^(1/12) ≈ 1.059;
2^(3/12) ≈ 1.189;
2^(7/12) ≈ 1.498,
etc.
- nth root {WP}

e.g., 12-tet:
2^(1/12) ≈ 1.059; 17-tet:
2^(1/17) ≈ 1.042; 31-tet:
2^(1/31) ≈ 1.023; etc.
- Calculator:
Logarithm
- Logarithm (log) {WP}
e.g.,
log10(1000) = 3, or 10^3 = 1000; log2(8)
= 3; i.e., 2^3 = 8; log10(3/2) = log10(1.5)
≈
0.176
- Cent (¢) {WP}
c = 1200 log2 (f2/f1)
e.g., 2/1 = 1200¢; 1/1 = 0¢
e.g., 2^(1/12) = 100¢; 3/2 ≈ 702¢; 4/3 ≈
498¢ (rounded to the nearest cent)
e.g., 81/80 ≈
21.5¢ (rounded
to the nearest 1/10 cent)
e.g., 5/4 ≈ 386.314¢ (rounded to 3 decimal places) {Calculator:
Wolfram
Alpha}
e.g., 6/5 ≈ 315.6¢ (rounded to 1 decimal place) {Calculator:
Wolfram
Alpha}
- Calculators:
 Geometry
Geometry
- Cartesian coordinate system {WP;
MW}
- Circle {WP;
MW}
- Dimension {WP}
- Euclid's Elements (c. 300 BCE) {WP;
Texas}
(Fitzpatrick 2008)
- Euclidean geometry {WP;
MW}
- Figurate number {MW}
- Triangular number {WP;
MW;
OEIS}
1, 3, 6, 10, 15, 21, ...
- Square number {WP;
MW;
OEIS}
0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, ...
- Fractal {WP;
MW}
- Plane {WP;
MW}
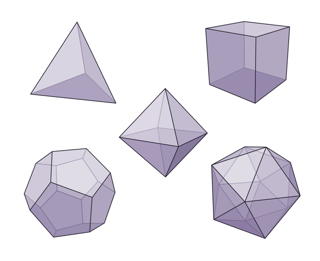
- Platonic solids {WP; MW}
- Polygon {WP;
MW}
- Pythagorean means {MW;
WP}
(Makeig 1981)
- Pythagorean theorem {WP;
MW}
- Rhombus {WP;
MW}
- Spiral {WP}
- Logarithmic spiral {WP;
MW}
- Tetractys {WP;
MW}
 Advanced
Advanced
- Binary tree {WP; MW}
- Continued fractions {WP;
MW}
- Coprime, or relatively prime, integers {WP;
MW}
- Farey sequence {WP; MW;
OEIS}
- Golden ratio {WP; MW}
- Group theory {WP; MW}
- Graph theory {WP; MW}
- Hasse diagram {WP; MW}
- Linear algebra {WP; MW}
- Mediant {WP;
MW}
- Multiplication table {WP;
MW}
- Number theory {WP; MW}
- Pascal's triangle {WP;
MW}
- Prime counting function {WP;
MW}
- Projective plane {WP;
MW}
- Rieman Zeta function {XW;
MW}
- Set theory {WP;
MW}
- Stern-Brocot tree {WP;
WP}
- Strähle construction {WP;
HFF}
- Tessellation, or tiling {WP; MW}
- Transfinite number {WP;
MW}
- Topology {WP;
MW}
- Torus {WP; MW}
* * *
Image credits: Click on an image to
see the image credit
Links
Sloane, Online Encyclopedia of Integer
Sequences {OEIS} –
https://oeis.org
Wikipedia {WP} –
https://www.wikipedia.org
Wolfram Alpha {WA} –
https://www.wolframalpha.com
Wolfram MathWorld {MW} –
https://mathworld.wolfram.com
Xenharmonic Wiki {WX} – https://en.xen.wiki
References
Benson, David. 2007. Music: A
Mathematical Offering. Cambridge: Cambridge University
Press. {GB;
Website}
Fauvel, John, Raymond Flood, and Robin Wilson, eds.
2003. Music and Mathematics: From Pythagoras to Fractals.
New York: Oxford University Press. {GB}
Gann, Kyle. 2019. The Arithmetic
of Listening: Tuning Theory and History for the Impractical
Musician. Urbana: University of Illinois Press. {GB; Full
text: TCL;
Audio Examples}
Hardy, G. H. and E. M. Wright.
2008/1936. An Introduction to the Theory of Numbers, 6th
ed. London: Oxford University Press. {GB}
Loy, Gareth. 2006. Musimathics: The
Mathematical Foundations of Music, Vol. 1-2. Cambridge,
Mass: MIT Press. {Full text: Vol. 1 Musical Elements:: TCL;
Vol. 2 Musical Signals: TCL}
Makeig,
Scott. 1981. "Means, Meaning, and Music: Pythagoras, Archytas, and
Plato." ex Tempore 1 (1981). {ucsd.edu}
Marecek, Lynn, MaryAnne Anthony-Smith, and Andrea Honeycutt
Mathis. 2020. Prealgebra, 2nd e. Houston, TX: OpenStax.
{OpenStax}
Mihăilescu, Preda and Daniel
Muzzulini. 2022. "A Diophantine equation concerning epimoric
ratios." European Mathematical Society Magazine 124
(2022): pp. 16–22. {EMS}
Sloane, N. J. A. 1964. The Online
Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences (OEIS). Available online
at: <https://oeis.org>.
Weisstein, Eric, ed. 2021. Wolfram
MathWorld – A Wolfram Web Resource. Available online at:
<https://mathworld.wolfram.com>.
Updated: March 6, 2025
 Number
Sets
Number
Sets Geometry
Geometry